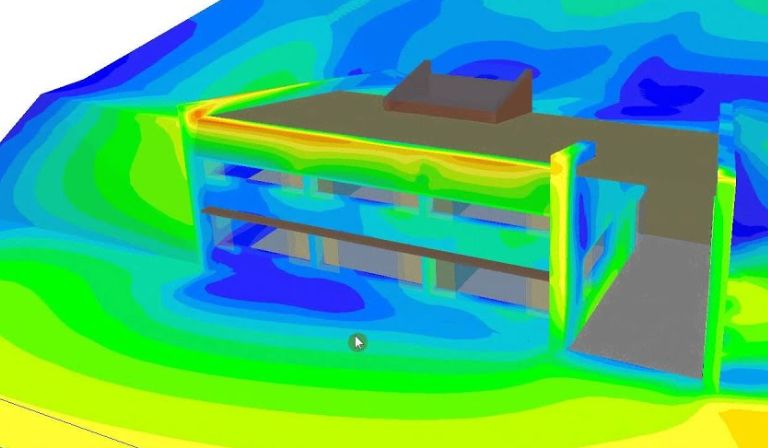
Phoenics, a computational fluid dynamics (CFD) software, is widely used in various fields for simulating fluid flow, heat transfer, and other physical processes. Its versatility makes it a valuable tool for engineers and scientists who need accurate simulations to design and optimize different systems. This article explores the fundamental principles of Phoenics, its applications, and how students and professionals can benefit from mastering this software.
Table of Contents
ToggleThe Basics of Computational Fluid Dynamics
To understand Phoenics, one must first grasp the basics of CFD. Computational fluid dynamics is a branch of fluid mechanics that uses numerical methods and algorithms to analyze and solve problems involving fluid flow. CFD software, such as Phoenics, allows users to create virtual simulations of fluid behavior in various environments, enabling detailed analysis and optimization.
CFD relies on three fundamental equations:
- The Continuity Equation: This ensures mass conservation in a fluid system.
- The Momentum Equation: Also known as the Navier-Stokes equations, these govern the motion of fluid particles.
- The Energy Equation: This describes the transfer of heat within a fluid.
Phoenics incorporates these equations and solves them using numerical methods, allowing users to visualize and predict fluid behavior with high accuracy.
Features and Capabilities of Phoenics
Phoenics offers a range of features that make it a powerful CFD tool:
- User-Friendly Interface: Unlike some CFD software that requires extensive programming knowledge, Phoenics provides a graphical user interface (GUI) that simplifies the setup of simulations.
- Flexible Grid System: The software supports structured and unstructured grids, enabling users to model complex geometries with ease.
- Robust Solver: Phoenics employs numerical solvers that efficiently handle various fluid flow scenarios, from laminar to turbulent flows.
- Multi-Physics Simulation: Beyond fluid flow, the software can simulate heat transfer, combustion, and chemical reactions.
- Customization and Scripting: Users can extend its capabilities through scripting and customization, making it suitable for specialized applications.
Applications of Phoenics in Different Industries
Aerospace Engineering
In the aerospace industry, Phoenics is employed to study airflow around aircraft bodies, optimize wing designs, and analyze propulsion systems. Engineers use it to enhance fuel efficiency and improve aerodynamics, leading to better-performing aircraft.
Automotive Industry
Automobile manufacturers utilize Phoenics to optimize vehicle aerodynamics, improve engine cooling, and analyze fuel combustion. By using CFD simulations, designers can reduce drag and enhance fuel economy without the need for extensive wind tunnel testing.
HVAC and Building Design
Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) engineers use Phoenics to design efficient ventilation systems, ensuring optimal air distribution within buildings. It helps architects and engineers optimize thermal comfort and energy efficiency in indoor environments.
Environmental Engineering
Phoenics plays a crucial role in environmental studies, such as modeling air pollution dispersion, predicting the behavior of natural water bodies, and assessing the impact of urban planning on wind flow patterns.
Marine and Offshore Engineering
The software is also used in marine engineering for studying ship hydrodynamics, designing offshore structures, and simulating wave interactions. Accurate CFD simulations help improve vessel stability and fuel efficiency.
Industrial Process Optimization
Many industries, such as chemical and pharmaceutical manufacturing, rely on Phoenics to optimize processes involving fluid mixing, heat exchange, and chemical reactions. This helps companies enhance product quality and reduce operational costs.
Learning and Mastering Phoenics
For students and professionals looking to master Phoenics, the following approach can be beneficial:
- Understanding CFD Fundamentals: Before diving into Phoenics, it is essential to have a strong grasp of fluid mechanics, thermodynamics, and numerical methods.
- Hands-On Practice: Practicing with real-world problems is key to mastering Phoenics.
- Exploring Online Resources: Numerous online courses, tutorials, and user forums offer guidance on using Phoenics effectively.
- Experimenting with Case Studies: Working on industry-relevant case studies helps bridge the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical application.
- Collaborating on Research Projects: Participating in research projects provides hands-on experience and exposure to real-world challenges.
Common Challenges and Solutions in Phoenics
While Phoenics is a powerful tool, users may encounter challenges when working with complex simulations. Here are some common issues and solutions:
- Mesh Quality Issues: Ensuring a well-structured mesh and refining grid resolution in critical areas can improve simulation accuracy.
- Convergence Problems: Adjusting solver settings and refining initial conditions can help achieve convergence.
- Long Computational Time: Utilizing parallel computing and optimizing solver settings can significantly reduce computation time.
- Interpreting Results Correctly: Comparing results with experimental data or known benchmarks can help validate the accuracy of the model.
Conclusion
Phoenics is a versatile and powerful CFD software that enables engineers and scientists to analyze fluid dynamics in various applications. Mastering this tool requires a combination of theoretical knowledge, practical experience, and continuous learning. Whether in aerospace, automotive, HVAC, or environmental engineering, the ability to simulate and optimize fluid flow can lead to significant advancements in design and efficiency. By overcoming challenges and refining their skills, users can leverage Phoenics to make informed decisions and drive innovation in their respective fields.